Satellite meeting for Transcription regulation
Topics
Biologists need to get more detailed information about what is happening a gene level when they look at microarray data:
- Enrichment analysis of TFBS
- Transcription factor binding site SNPs
- Histone binding
- Network analysis (which genes are interesting??)
- Expression levels
- siRNA, miRNA that control function
- Methylation
- Copy number variation
- Protein structure of TFs
Attendees
- Riu Yamashita
- Young Joo Kim
- Alberto Labarga
- Yulia Kovarskaya
Objective
Make a unified solution tool that biologists want in their functional, molecular studies. -Identify feasible techniques and economic solutions for them.
The questions that should be addressed.
1. Transcription binding sites, modulations
2. Histon binding sites
3. Histon modification
4. SNPs, SNP chips
5. Expression (mRNA or cDNA chips)
6. miRNA or RNAi
7. methylation (epigenetics)
8. CNV (copy number variation)
9. Protein structure
10. Protein chips
11. Tissue arrays
12. Cell-level functional studies
13. Pathway analysis
14. Next generation sequencing
15. OMIM or disease DB
16. Comparative genomics
17. Technologies unknown yet
How: Define each question in terms of biologists’ interests. Describe the limits of each question. Find the best or second best tools for each question. How to combine the questions for the sake of biologists (input and output data)
Proposed Solution
Use DAS'''
- You can find an introduction for the DAS system here
- The DAS workshop 2009 is just over, and there was some cool stuff there we could use DAS workshop2009
- What we want to achieve is quite similar to this: http://beta.gepas.bioinfo.cipf.es/pupasuite/www/index.jsp --Surely, it is really what I want. But it is to slow, so it is hard to analyze many times (Riu)
Results
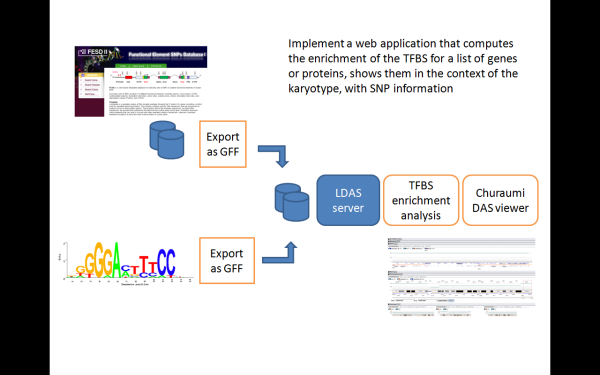
- Implemented a DAS layer for FESD II and the TFBS prediction systems
- Implemented a web application that computes the enrichment of the TFBS for a list of genes or proteins, and present the results using Ajax DAS viewer
Results
Future Plans
- Make some web server to evaluate the specific gene groups.
Attachments
-
churaumi2.png
 (59.6 KB) - added by alberto.labarga
16 years ago.
(59.6 KB) - added by alberto.labarga
16 years ago.
-
Pros and cons of the technologies available out there.doc
 (46.5 KB) - added by yjkim8
16 years ago.
(46.5 KB) - added by yjkim8
16 years ago.
Pros and cons of the technologies available out there